What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? How Does It Benefit Your Business
Learn what enterprise resource planning is, explore its types and differences so that you can drive efficient resource management and business growth.
Running a business means keeping track of a lot—finances, inventory, employees, and more. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) simplifies this by bringing all these processes into one system, making it easier to manage and coordinate everything. With ERP, you can see real-time data across your business, improve decision-making, and reduce the risk of errors.
In this article, we’ll explain what ERP is, how it works, and the different types available. We’ll also discuss the benefits of ERP, the industries that rely on it, and provide tips for choosing the right ERP solution for your business. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how ERP can add value to your organization.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) ?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a system that helps businesses manage and automate their core operations. Instead of using different tools for tasks like finance, HR, inventory, supply chain, and customer relations, ERP brings everything together into one platform. This makes it easier for companies to track and control all aspects of their business from a single place.
How Does ERP Work?
ERP systems have evolved from traditional software that required physical servers and manual data entry to modern, cloud-based platforms accessible via the web. Typically, the ERP provider manages the platform, while businesses rent access to its services.
To get started, businesses choose the ERP applications that fit their needs. These applications are then set up on the cloud servers, and the company works with the provider to integrate their processes and data into the system.
Once integrated, all departments can access real-time data from a centralized system, making information readily available to those who need it. With this data, businesses can generate reports, view performance metrics, and visualize key insights to better manage operations and make informed decisions.
Types of ERP Systems
When selecting an enterprise resource planning solution, it’s important to understand the different deployment models available. ERP systems generally fall into three main categories:
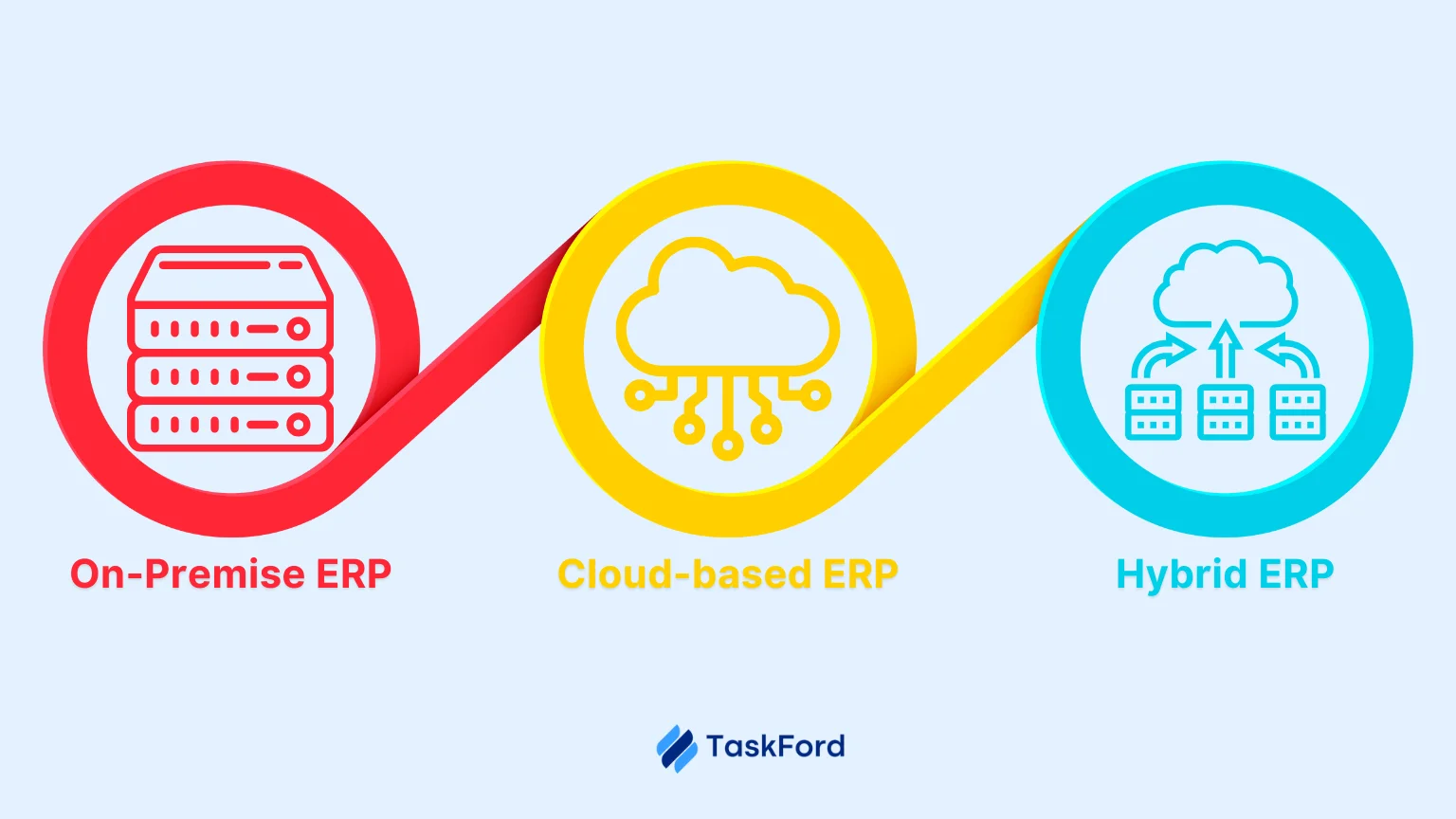
1. On-Premise ERP
On-premise ERP systems are installed locally on a company’s own servers and managed by the organization’s IT team.
- Advantages: Full control over data security and system customization. Extensive options for tailoring the system to meet specific business needs.
- Considerations: Requires a significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT resources. Longer implementation time and higher ongoing maintenance costs.
2. Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet, typically offered on a subscription basis.
- Advantages: Lower initial costs and predictable subscription fees. Faster implementation, scalability, and automatic updates handled by the vendor.
- Considerations: Less customization compared to on-premise solutions. Data security and compliance may depend on the vendor’s practices.
3. Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP solutions combine on-premise and cloud-based systems, allowing certain modules to be hosted on the cloud while others remain on local servers.
- Advantages: Flexibility to maintain sensitive data on-premise while leveraging cloud benefits for other functions. Balanced approach that can be tailored to the organization’s specific requirements.
- Considerations: Integration between cloud and on-premise components can be complex. Requires careful management to ensure seamless operation across environments.
Each ERP type offers unique benefits, and the right choice depends on your organization’s size, industry, and specific operational needs.
Differences Between ERP and Traditional Software
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and traditional software serve different purposes in business management. Here are the key differences:
- Scope and Integration
- ERP: An ERP system integrates various business functions such as finance, HR, inventory, and supply chain management into one platform. It provides a comprehensive, real-time view of business operations across departments.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software often focuses on specific tasks or departments. For example, accounting software may only handle financial data, and HR software may only focus on employee records. These tools usually operate separately, leading to siloed information.
- Data Management
- ERP: In an ERP system, all data is centralized in one database, ensuring that all departments have access to the same up-to-date information. This eliminates data redundancy and reduces the risk of errors.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software typically stores data separately, meaning each department or tool might have its own version of the same data. This can create inconsistencies and increase the risk of errors when data is transferred between systems.
- Automation and Efficiency
- ERP: ERP automates a wide range of business processes across various departments, reducing the need for manual input and improving overall efficiency. For example, it can automate order processing, inventory tracking, and financial reporting.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software typically automates tasks within a single function but does not provide a holistic approach. Each software may require manual input from other systems to complete processes that span multiple departments.
- Customization and Flexibility
- ERP: ERP systems are highly customizable to fit the specific needs of the business. They can be adapted to accommodate industry-specific requirements, business processes, and scale as the business grows.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software is often less flexible, as it is designed to handle specific tasks or functions without considering the broader scope of business operations.
- Real-Time Data and Reporting
- ERP: ERP systems provide real-time data and reporting across departments, helping business leaders make informed decisions quickly. Information is continuously updated, and reports are available at the click of a button.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software may not offer real-time data or integrated reporting. Instead, businesses often need to generate reports from different systems and manually compile information, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Cost and Implementation
- ERP: Implementing an ERP system can be expensive and time-consuming, especially for large organizations. It often requires significant upfront investment in software, hardware, and training.
- Traditional Software: Traditional software is usually more affordable and easier to implement. However, as businesses grow and need to integrate more software tools, costs can add up and lead to inefficiencies.
Here’s a summary of the differences between ERP and traditional software in a table format:
| Feature | ERP | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Scope & Integration | Integrates multiple functions into one platform | Focuses on specific tasks, operates separately |
| Data Management | Centralized data across departments | Data stored separately, leading to inconsistencies |
| Automation & Efficiency | Automates processes across departments | Automates within one department |
| Customization | Highly customizable to business needs | Limited customization, specific to functions |
| Real-Time Data & Reporting | Provides real-time, integrated reporting | Limited real-time data, manual reporting |
| Cost & Implementation | Expensive, complex to implement | Affordable, easier to implement |
Key Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning
Implementing an ERP system offers numerous benefits that can transform business operations:
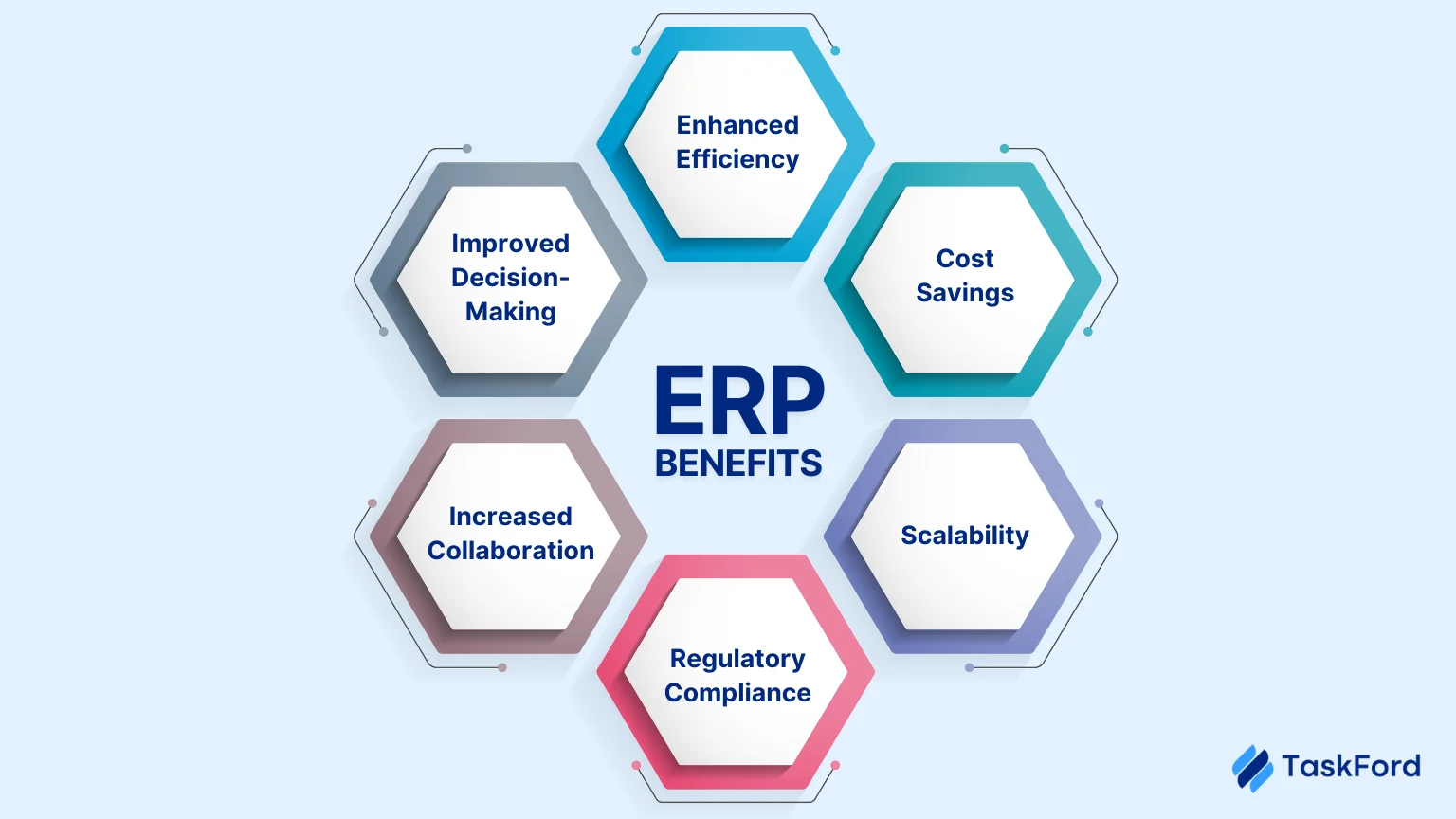
- Enhanced Efficiency: ERP systems streamline processes by automating routine tasks, reducing manual data entry, and eliminating redundancies.
- Improved Decision-Making: With real-time data and comprehensive analytics, leaders can make informed, data-driven decisions. When integrated with a data warehouse, ERP systems allow organizations to combine operational data with historical records for advanced reporting and strategic forecasting.
- Cost Savings: Better resource allocation and streamlined processes reduce operational costs and improve ROI.
- Increased Collaboration: A unified platform fosters better communication and collaboration across departments.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to grow with your business, accommodating increased workloads and new business processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Robust ERP solutions ensure adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Key Features to Look for in an ERP System
When evaluating ERP solutions, consider these essential features to ensure the system meets your organization’s needs:
- Real-Time Dashboards and Analytics: Get immediate insights into operations, enabling quick decision-making and proactive management.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the ERP can seamlessly connect with other tools such as CRM, HR software, and inventory systems.
- Customization and Flexibility: The system should be adaptable to your unique business processes.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive design is crucial for high user adoption and minimal training requirements.
- Scalability: Choose an ERP that can evolve with your business, supporting growth and expansion.
- Security and Compliance: Look for robust security features and compliance certifications to safeguard your data.
Famous ERP Tools on the Market
When it comes to choosing an ERP system, several well-known tools dominate the market. Each of these ERP platforms offers unique features tailored to different business needs:
- SAP ERP SAP is one of the most widely used ERP systems worldwide, known for its broad functionality across various industries. It offers comprehensive solutions for large enterprises, especially in manufacturing, retail, and finance sectors.
- Oracle ERP Cloud Oracle’s cloud-based ERP system integrates key business functions, such as finance, procurement, and project management, making it a solid choice for large and growing organizations looking for scalability and flexibility.
- Odoo Odoo is an open-source ERP platform offering a broad range of applications, from accounting to project management. Known for its flexibility and affordability, Odoo is a favorite among small to mid-sized businesses.
(Learn more: Free ERP Software for SME - Open Source Solutions That Work)
Each of these ERP solutions has distinct strengths, and comparing them can help you determine which one best aligns with your organization’s needs.
Also Worth Considering: Project-Centric Tools
While traditional ERP systems provide broad solutions for various business functions, project-centric tools focus on the specific needs of managing projects, tasks, and resources. These tools are designed for businesses that prioritize efficient project execution, team collaboration, and real-time tracking.
One such tool is TaskFord, an integrated work delivery platform that eliminates the gap between strategic goals and daily execution.
By unifying planning, resources, and communication, TaskFord enables organizations to move beyond simple tracking and achieve predictable delivery across all critical projects. It’s ideal for businesses looking to ensure alignment, improve efficiency, and guarantee that projects are completed on time and within scope. TaskFord complements traditional ERP systems by providing specialized support for project-driven operations, making it a valuable addition for companies that need to streamline project management.
Conclusion
Enterprise resource planning is far more than just a software solution—it is a strategic approach to unifying business processes, enhancing efficiency, and empowering organizations with real-time insights. ERP systems streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve decision-making, enabling companies to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, or consulting, an ERP system can transform the way you manage resources, break down silos, and respond to dynamic market demands. By integrating core functions into one centralized platform, ERP empowers you to make smarter decisions and achieve greater operational success.
Subscribe for Expert Tips
Unlock expert insights and stay ahead with TaskFord. Sign up now to receive valuable tips, strategies, and updates directly in your inbox.